Transformers
A deep learning model architecture for neural machine translation
Transformers are a type of neural network architecture that relies only on the attention mechanism. A transformer allows neural machine translation models to better handle the dependencies between the input and output sequences.
The transformer was first introduced in the paper titled ”Attention is all you need” by Google Research in 2017.
Architecture
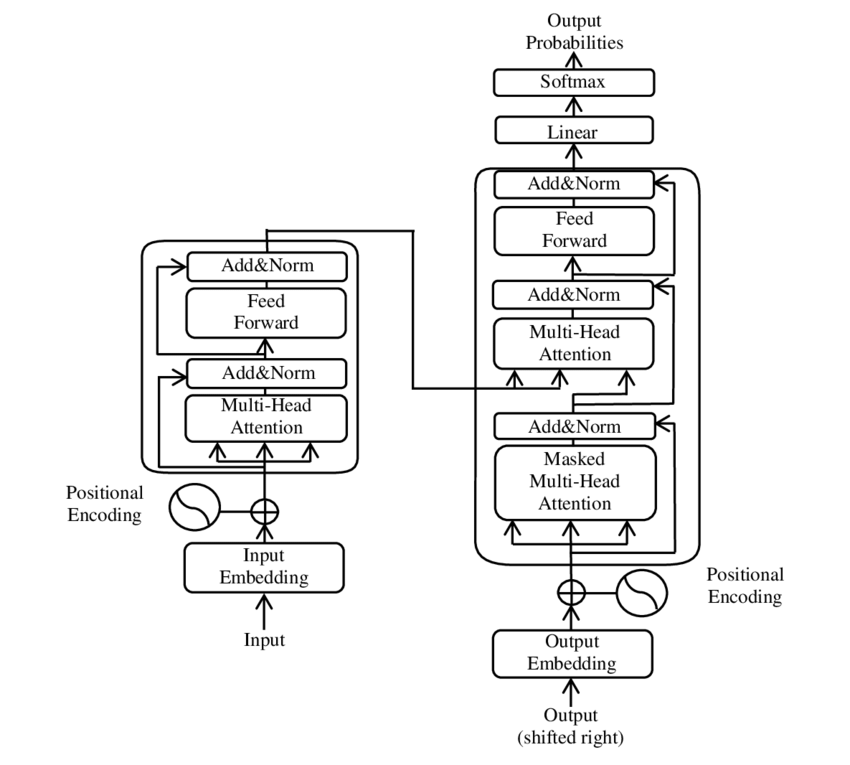
The transformer consists of an encoder and a decoder, which have several layers. These layers include sublayers of self-attention and feed-forward neural networks.
Image from the Transformers Wikipedia article
Encoder
The input sequence is first embedded into a continuous vector space and then passed through multiple self-attention layers. Each self-attention layer takes the input and creates a context vector based on the weighted sum of the input words. The generated output encoding then passes through a feed-forward neural network. The process is repeated for several layers. A normalisation step follows to produce the final hidden states. The encoder passes these hidden states to the decoder.
Decoder
The decoding process is similar to the one used in the encoder, as the decoder uses output sequence embeddings as its input. But in addition to the self-attention and feed-forward neural network layers, the decoder uses an additional mechanism called masked self-attention. It partially masks the output sequence to prevent the model from attending to the information on the subsequent positions.
Multi-head attention
Multi-head attention allows the model to attend to different parts of the input simultaneously. This improves the model’s ability to handle complex dependencies between input words and allows for fast processing.